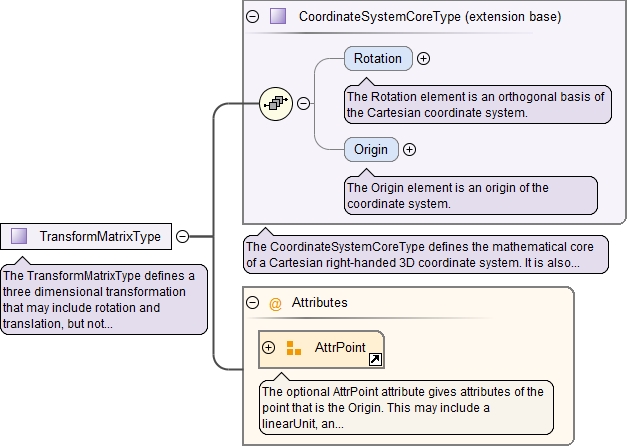
<xs:complexType name="TransformMatrixType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The TransformMatrixType defines a three dimensional transformation that may include rotation and translation, but not scaling. The vectors of the Rotation are unit vectors.</xs:documentation>
<xs:documentation>For any point, if: 1. The coordinates of the point in the "before" coordinate system are x, y, and z. 2. The coordinates of the point in the "after" coordinate system are X, Y, and Z. 3. The components of the XDirection are Xi, Xj, and Xk. 4. The components of the YDirection are Yi, Yj, and Yk. 5. The components of the ZDirection are Zi, Zj, and Zk. 6. The Cartesian coordinates of the Origin are Ox, Oy, and Oz. Then the following transformation equations hold. X = (Xi)x + (Yi)y + (Zi)z + Ox Y = (Xj)x + (Yj)y + (Zj)z + Oy Z = (Xk)x + (Yk)y + (Zk)z + Oz</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="CoordinateSystemCoreType">
<xs:attributeGroup ref="AttrPoint">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The optional AttrPoint attribute gives attributes of the point that is the Origin. This may include a linearUnit, an accuracy, etc.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attributeGroup>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType> |