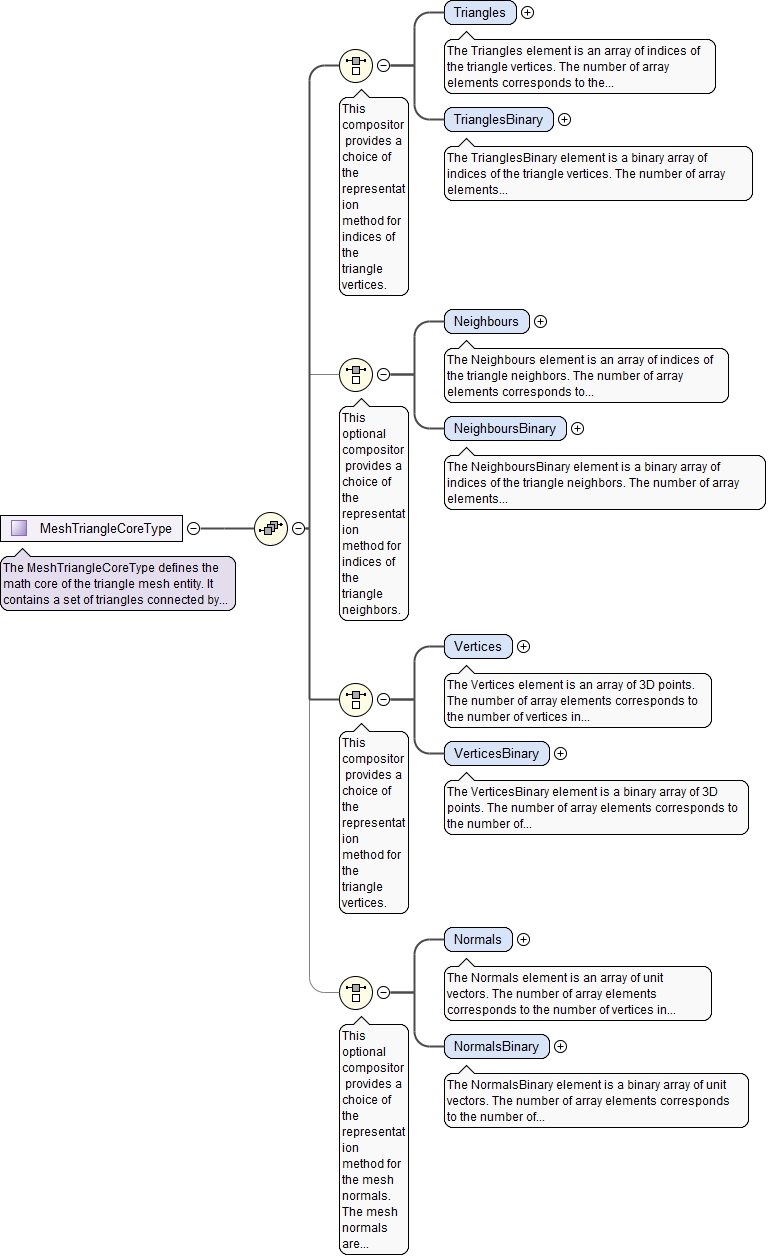
<xs:complexType name="MeshTriangleCoreType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The MeshTriangleCoreType defines the math core of the triangle mesh entity. It contains a set of triangles connected by their common edges.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>This compositor provides a choice of the representation method for indices of the triangle vertices.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
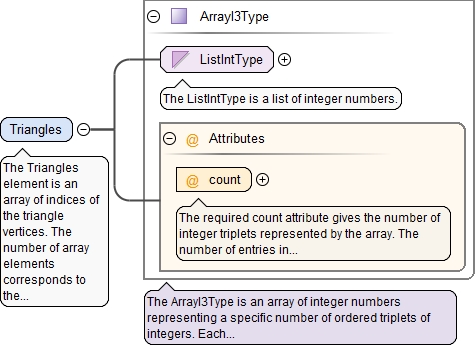
<xs:element name="Triangles" type="ArrayI3Type">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The Triangles element is an array of indices of the triangle vertices. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of triangles in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of integer numbers: index of the first vertex, index of the second vertex and index of the third vertex. All three vertex indexes of a triangle must be different and must lie in the range [0, ..., number of vertices - 1].</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
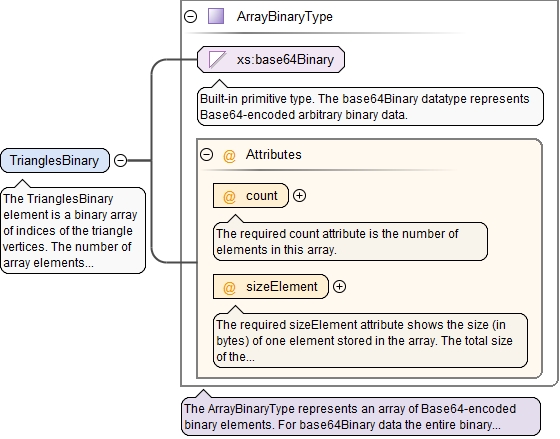
<xs:element name="TrianglesBinary" type="ArrayBinaryType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The TrianglesBinary element is a binary array of indices of the triangle vertices. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of triangles in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of 32-bit integer numbers: index of the first vertex, index of the second vertex and index of the third vertex. All three vertex indexes of a triangle must be different and must lie in the range [0, ..., number of vertices - 1].</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>This optional compositor provides a choice of the representation method for indices of the triangle neighbors.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
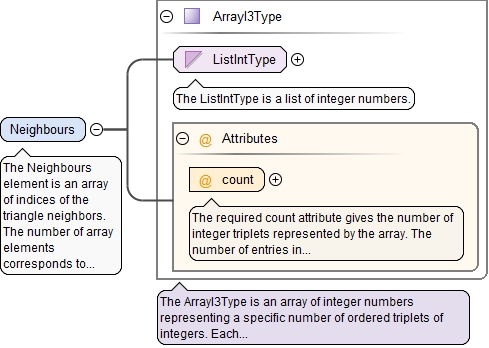
<xs:element name="Neighbours" type="ArrayI3Type">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The Neighbours element is an array of indices of the triangle neighbors. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of triangles in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of integer numbers: index of a neighbor triangle opposite to the first triangle vertex, index of a neighbor triangle opposite to the second triangle vertex, index of a neighbor triangle opposite to the third triangle vertex. There is a special index value "-1" which shows that there is no neighbor. The neighbor indices must lie in the range [-1,..., number of triangles - 1].</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
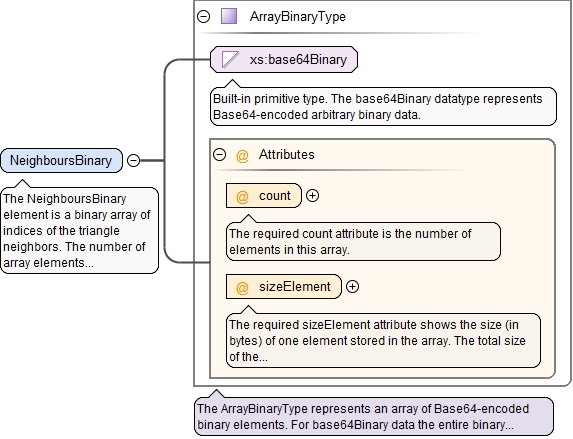
<xs:element name="NeighboursBinary" type="ArrayBinaryType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The NeighboursBinary element is a binary array of indices of the triangle neighbors. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of triangles in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of 32-bit integer numbers: index of a neighbor triangle opposite to the first triangle vertex, index of a neighbor triangle opposite to the second triangle vertex, index of a neighbor triangle opposite to the third triangle vertex. There is a special index value "-1" which shows that there is no neighbor. The neighbor indices must lie in the range [-1, ..., number of triangles - 1].</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>This compositor provides a choice of the representation method for the triangle vertices.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
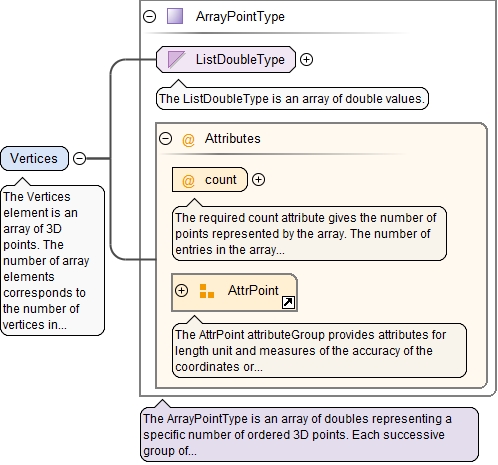
<xs:element name="Vertices" type="ArrayPointType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The Vertices element is an array of 3D points. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of vertices in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of real numbers: the X-coordinate, the Y-coordinate and the Z-coordinate.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
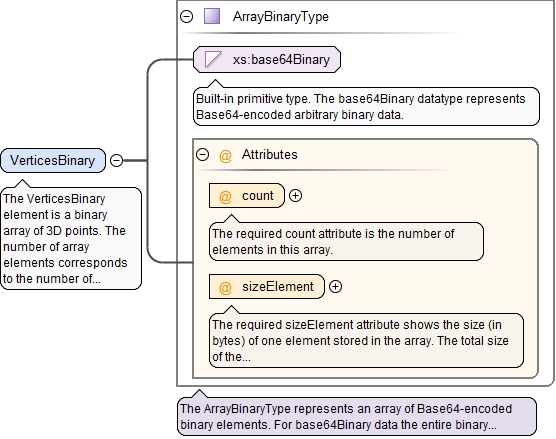
<xs:element name="VerticesBinary" type="ArrayBinaryType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The VerticesBinary element is a binary array of 3D points. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of vertices in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of real numbers (represented in accordance with the standard IEEE 754-2008): the X-coordinate, the Y-coordinate and the Z-coordinate.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>This optional compositor provides a choice of the representation method for the mesh normals. The mesh normals are defined at the mesh vertices and represent normals to the surface being approximated by the mesh.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
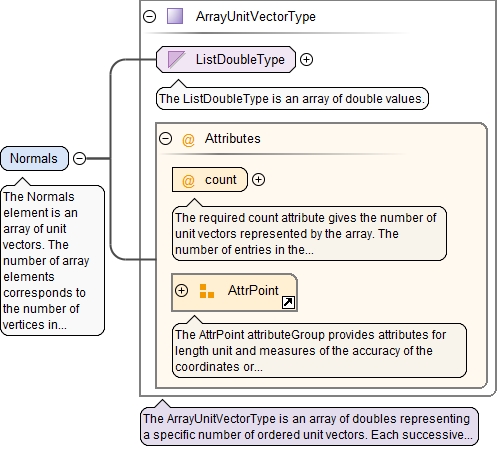
<xs:element name="Normals" type="ArrayUnitVectorType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The Normals element is an array of unit vectors. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of vertices in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of real numbers: the X-component, the Y-component and the Z-component.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
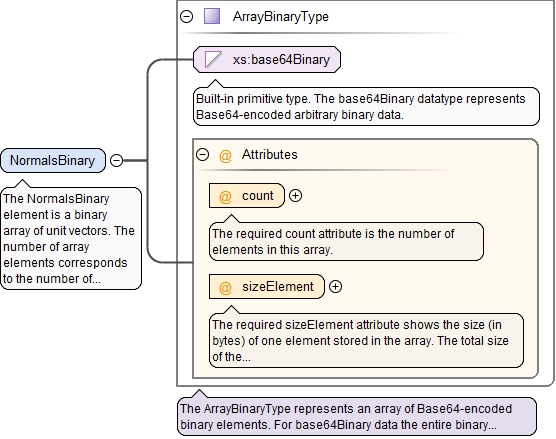
<xs:element name="NormalsBinary" type="ArrayBinaryType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The NormalsBinary element is a binary array of unit vectors. The number of array elements corresponds to the number of vertices in the mesh. Each element of this array is a triplet of real numbers (represented in accordance with the standard IEEE 754-2008): the X-component, the Y-component and the Z-component.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType> |